[et_pb_section fb_built=”1″ _builder_version=”4.16″ custom_padding=”||0px|||” global_colors_info=”{}” theme_builder_area=”post_content”][et_pb_row _builder_version=”4.16″ background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat” custom_padding=”8px||0px|||” global_colors_info=”{}” theme_builder_area=”post_content”][et_pb_column type=”4_4″ _builder_version=”4.16″ custom_padding=”|||” global_colors_info=”{}” custom_padding__hover=”|||” theme_builder_area=”post_content”][et_pb_text _builder_version=”4.27.4″ background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat” width=”100%” custom_padding=”|||1px||” global_colors_info=”{}” theme_builder_area=”post_content”]
In a constantly evolving industrial world, industrial performance is a key lever to ensure the competitiveness of businesses. Optimized management of production processes allows for increased productivity, improved quality, and reduced costs. It is with this in mind that Teeptrak offers innovative solutions that facilitate workshop management and continuous performance improvement. Through a data-driven approach and advanced tools, Teeptrak supports industries in their transformation toward greater efficiency.
Understanding Industrial Performance
What is industrial performance?
Industrial performance refers to a company’s ability to optimize its resources to meet production goals while ensuring quality and customer satisfaction. It relies on efficient management of processes and operations, enabling increased yield and better competitiveness. Today, industries rely on modern methods and tools to continuously improve their performance and meet market demands.
Key Indicators to Measure Industrial Performance
The evaluation of industrial performance relies on several key indicators. Among them is the Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), which measures equipment efficiency, as well as cycle time, which helps optimize production. Other indicators, such as non-compliance rates, team productivity, or production costs, provide a detailed view of performance. Analyzing this data helps implement improvement strategies tailored to the specific needs of each industry.
Our Solutions for Your Operational Excellence
Discover our all-in-one systems
Teeptrak’s solutions stand out for their integrated and modular approach, allowing for quick installation and intuitive use. With smart sensors and efficient software, our systems collect and analyze real-time data to offer precise monitoring of industrial performance. This ease of integration ensures a quick adaptation to business needs, whether it’s workshop management, process optimization, or team management.
The Role of Our Advanced Technology in Improving Your Processes
Technological innovation is at the heart of Teeptrak’s solutions. Our tools allow continuous monitoring of operations and provide detailed analysis to detect areas for improvement. By optimizing processes and facilitating decision-making, our solutions help reduce production downtime, increase quality, and better manage resources. This approach improves not only productivity but also customer satisfaction and business profitability.
Improvement Strategies with Teeptrak
Maximizing productivity with our modular solutions
One of the major advantages of Teeptrak’s solutions lies in their modularity. Every company faces specific challenges, and our tools adapt to these needs through customizable configurations. By optimizing production flows and providing real-time performance indicators, our solutions allow for the quick identification of improvement areas. This approach ensures better operation management and strategic decision-making to increase productivity while reducing losses.
Case Studies and Testimonials
Success stories: Increasing OEE and reducing downtime
Many industrial companies have seen a significant improvement in their OEE thanks to Teeptrak solutions. For example, an automotive parts manufacturer reduced downtime by 30% by optimizing workshop management. By identifying the causes of production losses in real time, the company was able to implement effective corrective actions, thus improving production quality and overall profitability.
How Our Clients Transformed Their Production with Teeptrak
Our customers testify to the tangible benefits of Teeptrak solutions. A company in the agri-food sector succeeded in boosting its industrial performance by improving the management of its key indicators. Using real-time data tools, it optimized its processes and strengthened collaboration between its teams. This transformation not only improved product quality, but also reduced operating costs by 15%, proving the strategic impact of our solutions.
Measure and Continuously Improve with Teeptrak
How to monitor your industrial performance in real time?
Thanks to its advanced technology, Teeptrak offers real-time monitoring of industrial processes. Our solutions collect and analyze production data, providing companies with a clear view of their operational management. By integrating these tools, businesses can identify gaps, adjust management practices, and maximize efficiency. This proactive approach enables strategic decision-making based on concrete indicators, ensuring continuous improvement.
Evaluate Your ROI Quickly with Our Dedicated Tools
Optimizing industrial performance also involves effective evaluation of return on investment (ROI). Our tools precisely measure the impact of changes made to production. By analyzing equipment usage rates, downtime reduction, and quality improvement, companies can justify their strategic choices. Our solutions offer precise management, ensuring measurable and sustainable productivity gains.
Training and Support from the Teeptrak Academy
Learn to master our solutions at your own pace
The Teeptrak Academy offers training tailored to the needs of each company. Whether you’re a manager, technician, or production supervisor, our programs help you acquire an in-depth understanding of our tools and methods. This personalized training ensures a quick integration of solutions and fosters better performance management in the workshop.
Free and Personalized Online Training for Our Clients
We offer free online training, accessible to all our clients. Adapted to various skill levels, it covers data management methods, performance indicator analysis, and industrial process optimization. With personalized support, each company benefits from effective learning to fully leverage Teeptrak’s features.
FAQ on Industrial Performance
What are the three types of improvement?
Industrial performance improvement relies on three main approaches:
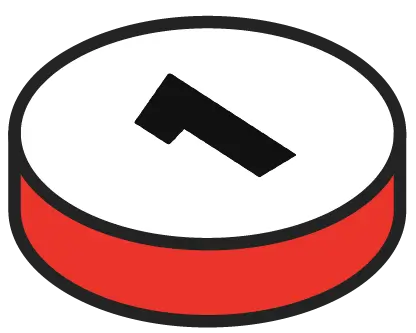 Continuous improvement (Lean, Kaizen), which consists in gradually optimizing processes.
Continuous improvement (Lean, Kaizen), which consists in gradually optimizing processes. Improvement through innovation, which relies on new technologies and tools.
Improvement through innovation, which relies on new technologies and tools. Improvement through disruption, which involves radical changes in methods or strategies to transform industrial management.
Improvement through disruption, which involves radical changes in methods or strategies to transform industrial management.
How to improve performance in a company?
To improve industrial performance, it’s essential to establish monitoring indicators and adopt proven methods such as Lean Management. Analyzing production data, training teams, and using advanced management tools allow for process optimization and increased operational efficiency.
What are the 4 steps of continuous improvement?
The PDCA cycle (Plan, Do, Check, Act) is a key model for improving performance:
Plan: Identify problems and set objectives for improvement.
Do: Implement solutions using a methodical approach.
Check: Measure results using indicators.
Act: Adjust and standardize best practices to ensure sustainable improvement.
What is industrial performance?
Industrial performance represents a company’s ability to maximize its operational efficiency by optimizing its resources. It relies on efficient management of processes, indicators, and tools, enabling high productivity levels and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Join the Industry Leaders who trust Teeptrak
Teeptrak already accompanies many industrial leaders in their quest for performance and operational excellence. Our innovative solutions enable optimized workshop management, continuous improvement of results and precise monitoring of indicators.
Join us today to transform your industrial strategy and reach new productivity targets!
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]


